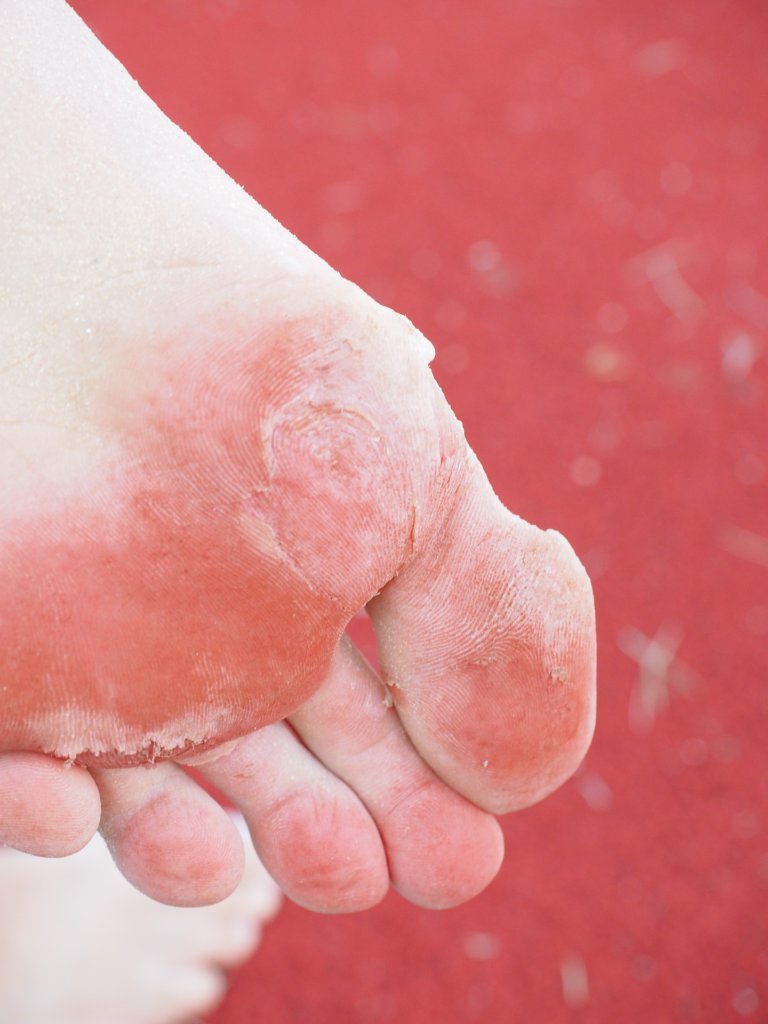
Athlete’s foot, also known as Tinea Pedis, is a skin disease caused by a fungus, usually occurring between the toes, but it can also affect other areas of the feet. Fingal infections are common on the feet because shoes create a warm, dark, and moist environment that encourages fungal growth.
Atlete’s foot Symptoms
The signs of athlete’s foot,include:
- Dry, flaky looking skin
- Itching and burning between the toes or other parts of the feet
- Scaling or peeling skin
- Inflammation or swelling
- Blisters, which often lead to cracking or peeling skin.
Athlete’s foot is an infectious disease and may spread to the soles of the feet and toenails. It may spread to other parts of the body by those who scratch the infected area and then touch themselves elsewhere.
When to visit a podiatric physician
If you believe that you have a fungus infection that does not respond to proper foot hygiene and there is no improvement within two weeks consult a podiatrist. If you are a diabetic consult a podiatrist as soon as you suspect you have athlete’s foot.
Athlete’s foot Diagnosis and Treatment
Your podiatrist will determine if a fungus is the cause of the problem. If it is, a treatment plan, including the prescription of antifungal medication, applied topically or taken by mouth, may usually be suggested. Such a treatment appears to provide better resolution of the problem when the patient follows the course of treatment prescribed by the podiatrist; if it’s shortened, failure of the treatment is common.
Topical or oral antifungal drugs are often prescribed.
If the infection is caused by bacteria and not fungus, antibiotics that are effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, such as penicillin, may be prescribed.
It is important to keep the feet dry by using foot powder in shoes and socks. The feet should be bathed frequently and all areas around the toes dried thoroughly.
If someone in your family develops athlete’s foot, disinfect home showers and tubs after each use to discourage transmission of infection.
Athlete’s foot prevention
You can prevent fungal infection by practicing the following:
- Wash feet daily with soap and water;
- dry carefully, especially between the toes
- Avoid walking barefoot
- Wear light and airy shoes
- Change shoes and socks regularly to decrease moisture
- Wear synthetic blend socks that wick away moisture
- Reduce perspiration – use talcum powder or antiperspirant on the feet